News

Read our latest news below, or sign up for our annual newsletter to keep up to date.
Newsletter #1 - 2020
Newsletter #2 - 2021
Newsletter #3 - 2023
Autism Without Boarders Award Event 2023
Both Artist and Researcher Celebrated at the 2023 ‘AUTISM WITHOUT BORDERS’ Award Event In 2023, the ‘AUTISM WITHOUT BORDERS’ Award was held at the Institute for Research Hospitalization and Health Care (IRCCS) in Pisa, Italy in November 2023. This Award was supported...
Art & Science Competition and Exhibition
To raise awareness about autism, challenge misconceptions, and promote neurodiversity, members of the Cambridge study team working on AIMS-2-TRIALS collaborated with a group of six autistic people and parents of autistic people (A-Reps) to design a creative project...
Bridging the gap: AIMS-2-TRIALS collaborators advocate for neurodiversity-affirming research
A groundbreaking shift is needed in the field of autism research to bridge a historical divide between researchers and the autistic community. A recent commentary, co-authored by experts from AIMS-2-TRIALS in collaboration with international institutions and Autism...
AIMS-2-TRIALS is in the ‘Top 10’ IMI Projects
A recent report published by the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI), the world’s largest public-private partnership in the life sciences, showed that AIMS-2-TRIALS have published the most papers out of all Phase 2 IMI-funded projects. Since the IMI was launched,...
New Project: European Autism Genomics Registry
The genetics of autism are very complex. Some autistic people have a genetic syndrome associated with autism, like Angelman syndrome or dup15q syndrome, whilst others do not. Given the diversity of autism, it is important that research looks at the broad range of...
Studying male and female brains: do they differ between autistic and non-autistic people?
Extensive research shows that far more male individuals are diagnosed as autistic, compared to females. This autism ‘sex-ratio bias’ means that around 4 more males are identified as autistic than females. So why is there a higher diagnosis rate for autism in males?...
AIMS-2-TRIALS consultation on data sharing
Sharing scientific research data is important because it can help improve the quality, usefulness, and reliability of research. For example, it enables scientists to analyse larger data sets, which increases their ability to uncover patterns in the data. Data sharing...
Autistic people may pay less attention to faces due to the way their brains process sensory information
Extensive research has shown that autistic people mostly pay less attention to social cues compared to non-autistic people. Previous research has shown that on average, autistic people generally spend less time looking at faces, and especially eyes, during social...
Understanding autism: Linking genetics, brain structure and behaviour
Scientists still do not know what underpins the core behavioural characteristics of autism, for example repetitive behaviours. One well-supported theory suggests that these behaviours stem from an imbalance between neurotransmitters (the ’chemical messengers’ in the...
Recognising faces: microstates
AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers have been exploring how people process faces, both in autistic and non-autistic individuals. Previous research has shown that most people find it trickier to recognise upside down (inverted) faces compared to upright faces (see image on the...
Measuring brain activity may help tailor support for autistic people
AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers, as part of a large-scale collaboration in the Longitudinal European Autism Project (LEAP), have been studying the variability within autism. In a large study of over 400 children and adults, the team have found that the timing of the N170 –...
AIMS-2-TRIALS Work Package Updates for 2022
Research studies across the lifespan Project updates: Over the past year, recruitment of participants and families to our AIMS-2-TRIALS cohort studies has grown at its most significant rate since pandemic-related restrictions on face-to-face research eased. The Leads...
Reviewing the evidence for medications and dietary supplements to support autistic people
Everyone experiences the world differently and faces different challenges. Some autistic people may want support with difficulties in areas such as sleep, social interaction, sensory difficulties, irritability, or depression, while others may not. Currently, no...
Exploring the brain biology of people with rare genetic conditions related to autism
Much remains unknown about the biology and genetics of autism, although researchers have shown that it is heritable and there are many genes linked to its development. One unique approach to discovering more is to study rare genetic conditions that often co-occur with...
The Value of Treatment
Find out about the outcome of our research projects looking at care pathways for autism and autism with co-occurring epilepsy, including data from the UK, Spain and Italy. We explore treatment gaps/unmet needs, screening and diagnosis times, funding and make...
Variation in brain structure is linked to changes in adaptive behaviour in autistic people
A new large-scale AIMS-2-TRIALS study is the first to show a link between brain structure and the later development of ‘adaptive behaviour’ in autistic people. Adaptive behaviours are important skills that help people get by in their everyday lives, and their...
AIMS-2-TRIALS Partners involved in Lancet Commission
The Lancet has launched a first-of-its-kind Commission that “aims to answer the question of what can be done in the next 5 years to address the current needs of autistic individuals and families worldwide.” The Commission’s 32 representatives are co-led by Prof Tony...
Attention in infants is linked to differences in biological sex and socio-economic status
AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers have found that an infant’s ability to flexibly switch their gaze from one object to another (visual disengagement) differs based on their biological sex (male/female) and their socio-economic status (a measure of how income, education, and...
Closer collaborations needed between scientists and the autistic community
AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers, in partnership with ethicists at the University of Oxford and scientists at McGill University, have reviewed the ethics surrounding ‘early autism research’. This field of research identifies early changes in the developing brain (so-called...
Infants’ brain activity when seeing faces is written in their DNA
Infants with more of the genetic differences related to autism were found to respond to faces differently, even at a very young age, before signs of autism might be noticeable.Many thanks to Birkbeck for allowing us to reprint this article about AIMS-2-TRIALS...
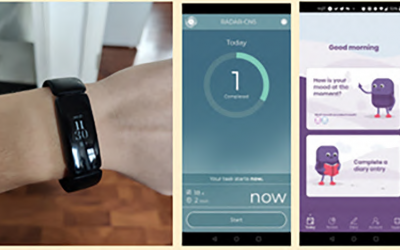
Developing wearable technology with involvement from autistic people
AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers are working alongside autistic people to develop technology that objectively measures aspects of their experience. Wearable devices, such as smart watches, can include sensors to record information like heart rate and skin conductivity and...