Innovation Radar is a European Commission initiative to identify innovations and innovators in EU-funded research. AIMS-2-TRIALS recently submitted several important developments to the scheme, receiving positive feedback and inclusion within the Innovation Radar website at a range of levels of readiness, as laid out in the diagram below.
Included are innovations in stem cell research that are important for drug discovery, a multidisciplinary data-sharing platform and tools for clinical and translational research.
Expand the headings below to read details about each of the AIMS-2-TRIALS innovations included.
For more details about the Innovation Radar scheme, visit the official website via https://www.innoradar.eu/about
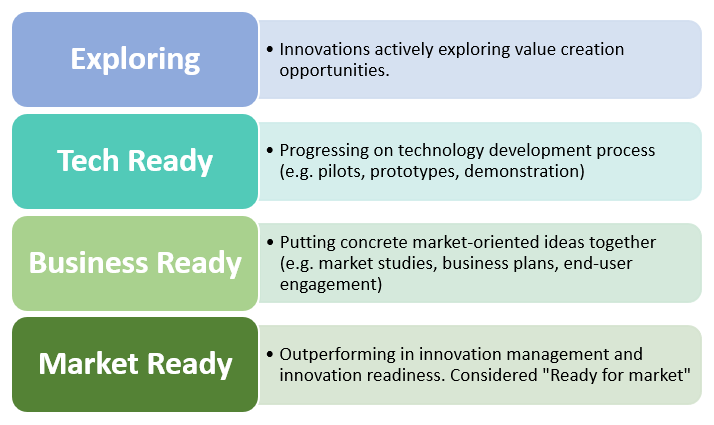
The levels of innovation as identified by Innovation Radar
Women-led innovation
Innovation Radar also identifies developments in which a woman had a leadership role in at least one of the organisations involved. Four of the six AIMS-2-TRIALS initiatives included have been identified as ‘women-led innovations’.
All AIMS-2-TRIALS innovations are under continued development, with particular emphasis on ensuring their relevance for the autism community – for example, through enhancing autism research or extending to clinical settings to support autistic people and their families.
Stem Cell reprogramming at scale - Market ready
 A key challenge holding back progress in developing and screening new drugs is the slow process of generating pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). This new technique, developed by AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers, enables brain neurons to be grown from human blood, skin or hair cells, which have the same genetic characteristics to the person from whom the cells was taken. Researchers can therefore explore characteristics of the brain cells in the lab. This development will enable new applications of this technique in research including understanding potential subgroups of people that may benefit from certain therapies or treatments.
A key challenge holding back progress in developing and screening new drugs is the slow process of generating pluripotent stem cells (iPSC). This new technique, developed by AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers, enables brain neurons to be grown from human blood, skin or hair cells, which have the same genetic characteristics to the person from whom the cells was taken. Researchers can therefore explore characteristics of the brain cells in the lab. This development will enable new applications of this technique in research including understanding potential subgroups of people that may benefit from certain therapies or treatments.
Prof Cader leads iPSC work in AIMS-2-TRIALS and discovered a way to greatly increase the speed and quality of iPSC call production iPSCs. He commercialised this new knowledge by founding a new SME – Oxford StemTech Ltd (https://www.oxfordstemtech.com/)
https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39922
Key organisations:
- Oxford StemTech Ltd
- University of Oxford
The Smart Baby Suit: a novel system to monitor infants at home - Business ready
In clinical and intervention research, there is a pressing need for tools that can monitor behavioural and physiological change in naturalistic settings, from early development and over time.
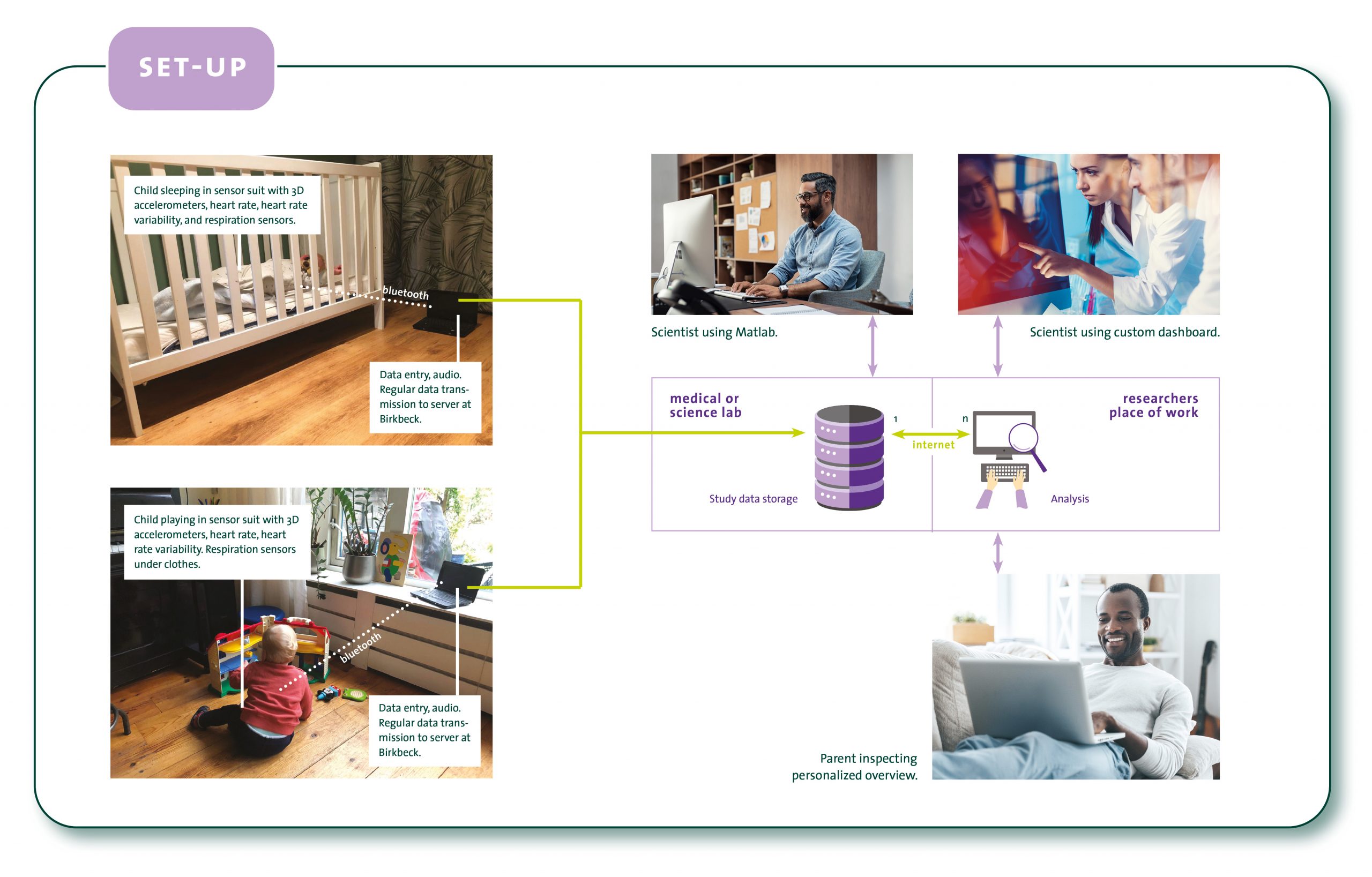 AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers have developed a novel, comfortable and easy to use Smart Baby Suit – initially developed for use with infants at elevated likelihood for autism – which is sensitive to heart rate, heart rate variability, breathing rate and movement in the home environment.
AIMS-2-TRIALS researchers have developed a novel, comfortable and easy to use Smart Baby Suit – initially developed for use with infants at elevated likelihood for autism – which is sensitive to heart rate, heart rate variability, breathing rate and movement in the home environment.
The baby suit securely transmits data to the researchers, where Artificial Intelligence-based software provides insights into the behavioural and cognitive development of babies in their natural surroundings.
https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39924
Key organisations:
- Noldus Information Technology
- Demcon
- Birkbeck College, University of London
ExperienceLab translates into the clinical domain - Exploring
AIMS-2-TRIALS partner Starlab provides cost-effective, direct measures of brain activity based on EEG (electroencephalogram – a non-invasive way to record brain activity). One of their platforms, ExperienceLab, characterizes the emotional response of users from their brain signals.

Starlab has developed an EEG-based marker related to emotional processing and emotion regulation, which is being validated as part of AIMS-2-TRIALS research with the aim of better understanding autism features across different age groups.
In addition, Starlab is investigating the feasibility of applying other ExperienceLab features, such as measures of attention and engagement, to distinguish social/ non-social processing abilities in a group of children with autism symptoms within the Safe Passage study in South Africa. These developments have important implications for the use of this tool in clinical trials, including across small- and middle-income countries.
 https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39925
https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39925
Key organisations:
- Starlab
TaskEngine: An integrated platform for neurocognitive assessment in clinical neuroscience - Exploring
 To enable direct measures of brain function to be useful in psychiatry, there is a need to move beyond small-scale research studies using study-unique tasks, stimuli and analysis approaches.
To enable direct measures of brain function to be useful in psychiatry, there is a need to move beyond small-scale research studies using study-unique tasks, stimuli and analysis approaches.
Task Engine is a suite of software libraries developed by AIMS-2-TRIALS partner Birkbeck, University of London, for the standardisation and automation of data collection and analysis for multisite neurocognitive data collection. TaskEngine provides a platform for incorporating neurocognitive assessment into clinical studies. This allows researchers to generate robust and reliable biomarkers that in turn could improve outcomes for people with neurodevelopmental/ psychiatric conditions. This could be achieved, for example, through more effective support, better tailored to each individuals’ profiles of strengths and difficulties.
 https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39927
https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39927
Key organisations:
- Birkbeck, University of London
‘Seeing’ an individual’s drug response in autism - Market ready
Different people respond differently to medications, so tools are needed that can be used to measure an individuals brain response to a drug. This will aid development of what’s referred to as ‘personalised medicine’. Researchers at King’s College London have developed a passive Sensitivity Index based on a simple visual EEG task (electroencephalogram – a non-invasive way to record brain activity), which can distinguish between those with and without an autism diagnosis at an accuracy of 70% in proof of concept studies. The Sensitivity Index also captures change in visual processing in response to a test dose of medication, making it a potential stratification tool to identify those who are most likely to respond to treatment. The passive nature of the Sensitivity Index means that it may be applicable and feasible for use across a wide range of ages and cognitive abilities. This innovation is now being developed for use with using virtual reality goggles to ensure every participant experiences the same test environment, regardless of where testing takes place.
This innovation is now being developed for use with using virtual reality goggles to ensure every participant experiences the same test environment, regardless of where testing takes place.
 https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39928
https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39928
Key organisations:
- King’s College London
OWEY: accelerating global precision medicine efforts via integration of multidisciplinary big datasets - Market ready
 A key barrier to international data sharing in autism research is the lack of a secure infrastructure that allows ‘real time’ data deposition and examination. Developed as part of AIMS-2-TRIALS, OWEY is a unique database infrastructure that allows datasets to be continuously uploaded, as each participant is enrolled to a research or clinical study.
A key barrier to international data sharing in autism research is the lack of a secure infrastructure that allows ‘real time’ data deposition and examination. Developed as part of AIMS-2-TRIALS, OWEY is a unique database infrastructure that allows datasets to be continuously uploaded, as each participant is enrolled to a research or clinical study.
Through its high level of automation, OWEY delivers – almost instantaneously – pseudononymised (meaning with participant ID coded), documented datasets that are aggregated with previously uploaded data. OWEY is designed to ensure the data security both regarding the storage and sharing of large, multidisciplinary datasets.
OWEY thus has the potential to foster global precision medicine research by removing geographical borders, data sharing delays and technical challenges linked to the size of innovative large datasets while ensuring compliance with the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
 https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39930
https://www.innoradar.eu/innovation/39930
Key organisations:
- Institut Pasteur
- Clinical Research Associates/Simons Foundation
Published 28 June 2021